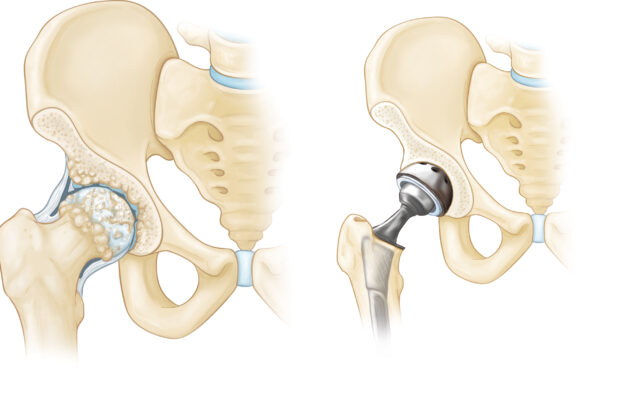
Joint replacement surgery has become very common these days and people across the world go for this surgery. It offers an improved quality of life to patients suffering from severe joint pain that leads to immobility in them. As you must be aware that everything has its pros and cons, similarly, there is always a possibility for patients getting joint replacement surgery done to fall prey to infections in their joints. However, the chances for joint replacement infection are very less but still 1-3% of people can become victims of this.

Joint replacement infection generally occurs in the wound or in the surrounding area of the artificial joints. This infection may happen post-surgery in the hospital itself or when you go back home. At times, infection occurs years after the surgery and requires immediate attention so that situations don’t become severe. An infection in your body mainly occurs due to the attack of bacteria. In majority of the cases when bacteria attack your bloodstream, your immune system acts promptly and kills those bacteria. But when this bacteria reaches artificial implants made of plastic or metal and invades that area, it becomes difficult for your immune system to eliminate it. As a result, bacteria multiply in this region and cause infection. Your doctor will give you medications to treat the infection, but in cases when these medicines cause no good to the patient then re-surgery is done to eradicate the infection completely.
When a person suffers from joint replacement infection, he faces certain symptoms that includes,
- Severe pain, discomfort, stiffness and swelling in the joint
- Tiredness
- Redness in the area surrounding the wound
- Consistent fever
- Night sweat
When the patient notices the above symptoms, he should immediately go to the doctor for the diagnosis of the problem. If infection is detected in the early stages then it can be treated successfully and the implants can be retained. Your doctor will perform various imaging tests like X-ray, bone scans and laboratory tests like blood tests, analysing fluid in your joints etc to detect the root cause of the problem. Depending on the extent to which infection is spread and your health conditions, your doctor will suggest the treatment plan. If the infection is present just on the tissues surrounding the artificial joint and not deep inside the joint then your doctor will prescribe oral medicines like antibiotics. In case infection has gone beyond the tissues and has deeply affected the artificial joints, then surgery is done to get relief. Taking preventive measures can help the person in avoiding joint replacement infections.